A sampling of inventors and their inventions from Greece
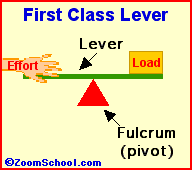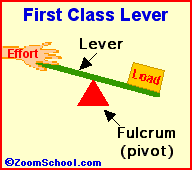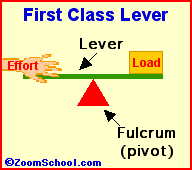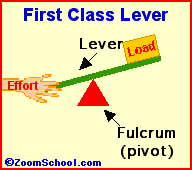
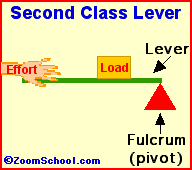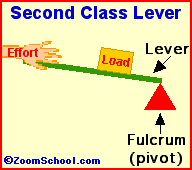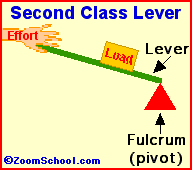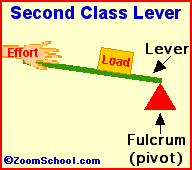
Archimedes (287-212 BC) was a prolific ancient Greek mathematician. Archimedes invented the water screw, a device for raising water using an encased screw open at both ends. The screw is set an an angle, and as the screw turns, water fills the air pockets and is transported upwards. The Archimedes screw is still in use today. Among his many accomplishments was the first description of the lever (around 260 BC). Levers are one of the basic tools; they were probably used in prehistoric times. Many of our basic tools use levers, including scissors (two class-1 levers), pliers (two class-1 levers), hammer claws (one class-1 lever), nutcrackers (two class-2 levers), and tongs (two class-3 levers).

An astrolabe is an instrument that was used to determine the altitude of objects in the sky (like the sun or stars). It was first used around 200 B.C. by astronomers in Greece. The astrolabe was replaced by the sextant.
The catapult is a device that hurls heavy objects or arrows over a large distance. It was invented in ancient Greece in 399 BC by Dionysius the Elder of Syracuse. The Romans later added wheels to the catapult to make it more maneuverable. The catapult (also called the ballista) was a major weapon of warfare for well over a thousand years. A double-armed catapult (also called the trebuchet) was invented by Mariano Taccola of Siena during the Middle Ages, about AD 1400.
The catapult was invented in ancient Greece (in 399 BC) by Dionysius the Elder of Syracuse. The catapult is a device that hurls heavy objects or arrows over a large distance. The Romans later added wheels to the catapult to make it more maneuverable. Also called the ballista, this device was a major weapon of warfare for well over a thousand years. A double-armed catapult (also called the trebuchet) was invented by Mariano Taccola of Siena during the Middle Ages, about AD 1400.
The steam engine was invented by Heron, an ancient Greek geometer and engineer from Alexandria. Heron lived during the first century AD and is sometimes called Hero. Heron made the steam engine as a toy, and called his device “aeolipile,” which means “wind ball” in Greek. The steam was supplied by a sealed pot filled with water and placed over a fire. Two tubes came up from the pot, letting the steam flow into a spherical ball of metal. The metallic sphere had two curved outlet tubes, which vented steam. As the steam went through the series of tubes, the metal sphere rotated. The Greeks never used this remarkable device for anything but a novelty. A steam engine designed for real work wasn’t designed until 1690, when Dionysius Papin published plans for a for a high-pressure steam engine. Thomas Savery built the first steam engine in 1698. James Watt later improved the steam engine.
Levers are one of the basic tools; they were probably used in prehistoric times. Levers were first described about 260 BC by the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes (287-212 BC). Many of our basic tools use levers, including scissors (two class-1 levers), pliers (two class-1 levers), hammer claws (one class-1 lever), nutcrackers (two class-2 levers), and tongs (two class-3 levers).



The steam engine was invented by Heron, an ancient Greek geometer and engineer from Alexandria. Heron lived during the first century AD and is sometimes called Hero. Heron made the steam engine as a toy, and called his device “aeolipile,” which means “wind ball” in Greek. The steam was supplied by a sealed pot filled with water and placed over a fire. Two tubes came up from the pot, letting the steam flow into a spherical ball of metal. The metallic sphere had two curved outlet tubes, which vented steam. As the steam went through the series of tubes, the metal sphere rotated. The aeolipile is the first known device to transform steam power into rotary motion. The Greeks never used this remarkable device for anything but a novelty. A steam engine designed for real work wasn’t designed until 1690, when Dionysius Papin published plans for a for a high-pressure steam engine. Thomas Savery built the first steam engine in 1698. Watt later improved the steam engine.
The umbrella was invented thousands of years ago. The earliest umbrellas were made to shade the user from the sun (an umbrella used as a sun shade is called a parasol). Umbrellas were used as much a 4,000 years ago in ancient Assyria, China, Egypt, and Greece. The Chinese were probably the first to waterproof the umbrella for use in the rain; they used wax and lacquer (a type of paint) to repel the rain. Samuel Fox (1815 - 1887), an English inventor and manufacturer, invented the steel ribbed umbrella in 1852 (wood or whale bone had been used before this).
