Glossary of Inventors and Inventions starting with the letter L.
The first incandescent electric light was made in 1800 by Humphry Davy, an English scientist. He experimented with electricity and invented an electric battery. When he connected wires to his battery and a piece of carbon, the carbon glowed, producing light. This is called an electric arc.
Much later, in 1860, the English physicist Sir Joseph Wilson Swan (1828-1914) was determined to devise a practical, long-lasting electric light. He found that a carbon paper filament worked well, but burned up quickly. In 1878, he demonstrated his new electric lamps in Newcastle, England.
The inventor Thomas Alva Edison (in the USA) experimented with thousands of different filaments to find just the right materials to glow well and be long-lasting. In 1879, Edison discovered that a carbon filament in an oxygen-free bulb glowed but did not burn up for 40 hours. Edison eventually produced a bulb that could glow for over 1500 hours. The incandescent bulb revolutionized the world.
Edwin Herbert Land (1909-1991) was an American physicist and inventor who developed the first modern light polarizers (which eliminate glare) and other optical devices, investigated the mechanisms of color perception, and developed the instant photography process (the Polaroid camera). Land established the Polaroid Corp. in 1937.
Latex (a natural, stretchy substance from which rubber is made) is extracted from rubber trees. Rubber trees are large trees (belonging to the spurge family, family Euphorbiaceae) that live in tropical (warm) areas. These trees are tapped for their latex, which is produced in their bark layers (latex is not the sap). The Pará rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis) is native to South American rain forests, and grows to be over 100 ft (30 m) tall. In 1876, Henry Wickham brought seeds from the Para rubber tree (taken from the lower Amazon area of Brazil) to London, England. Seedlings were grown in London, and later sent to Ceylon and Singapore. The technique of tapping rubber trees for their latex was developed in southeast Asia (before that, the trees were cut down to extract the rubber). Commercial rubber production now takes place in Malaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, and Sri Lanka (but not significantly in South America).
Lewis Howard Latimer (1848-1928) was an African-American inventor who was a member of Edison’s research team, which was called “Edison’s Pioneers.” Latimer improved the newly-invented incandescent light bulb by inventing a carbon filament (which he patented in 1881).
The first lawn mower was invented in 1830 by Edwin Beard Budding. Budding (1795-1846) was an engineer from Stroud, Gloucestershire, England. His reel mower was a set of blades set in a cylinder on two wheels. When you push the lawn mower, the cylinder rotates, and the blades cut the grass. Budding patented his lawn mower on August 31, 1830. Before his invention, a scythe was used (or sheep or other grazing animals were allowed to graze on the grass). The first reel lawn mower patent in the US (January 12, 1868) was granted to Amariah M. Hills, who formed the Archimedean Lawn Mower Co.
The dry cell is a an improved voltaic cell (battery) that has a cylindrical zinc shell (the zinc acts as both the cathode and the container) that is lined with an ammonium chloride (the electrolyte) saturated material (and not a liquid). Although called dry, dry cells are not entirely dry, but they are less bulky and more easily transported than earlier batteries. The dry cell battery was developed in the 1870s-1870s by Georges Leclanché (1839-1882), a French engineer, who used an electrolyte in the form of a paste in his new battery.
Legos (TM) are a very popular interlocking plastic toy. The LEGO toy company was founded by Ole Kirk Christiansen of Denmark in 1932, but the company then sold mostly wooden toys. The word LEGO was formed from two Danish words, “LEg GOdt,” which mean “play well.” Christiansen was a carpenter from the Danish village of Billund. The interlocking plastic blocks (the stud and tube coupling system) were invented by Godtfred Christiansen (Ole’s son), and patented in 1958. Lego toys were first sold in the USA in 1961. LEGO people were introduced in 1974.
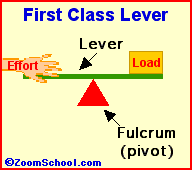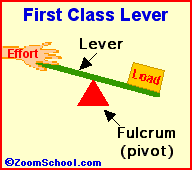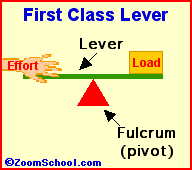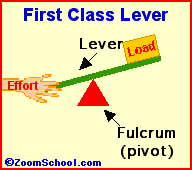
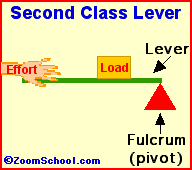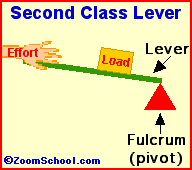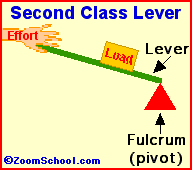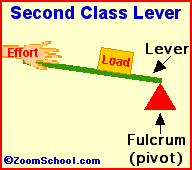
Levers are one of the basic tools; they were probably used in prehistoric times. Levers were first described about 260 BC by the ancient Greek mathematician Archimedes (287-212 BC). Many of our basic tools use levers, including scissors (two class-1 levers), pliers (two class-1 levers), hammer claws (one class-1 lever), nutcrackers (two class-2 levers), and tongs (two class-3 levers).

The candy called “Life Savers” was invented in 1912 by Clarence Crane, a chocolate maker from Cleveland, Ohio. His original Life Saver was a life-preserver-shaped peppermint candy called “Pep-O-Mint.” Crane designed it as a summer candy - one that would not melt in the summer heat. He bought a pill-making machine to make the candies, and then punched a hole in the middle. Since they looked like little life preservers, he called them Life Savers. In 1913, he sold the rights to his candy to Edward Noble for only $2,900. Noble then sold Life Savers in many flavors, including the original peppermint. There are now 24 flavors; they are manufactured in Holland, Michigan.

Lincoln Logs are a popular children’s toy building set that consists of interlocking notched logs. Children can easily make log cabins and other structures from the tiny wooden logs.
Lincoln Logs were invented in 1916 by John Lloyd Wright (1892-1972), an architect and one of the five children of the world-famous architect Frank Lloyd Wright. John patented his toy in 1920, and sold the logs through his toy company, the Red Square Toy Company. Playskool bought the rights to Lincoln Logs in 1943.
Hans Lippershey (1570-1619) was a German-born Dutch lens maker who demonstrated the first refracting telescope in 1608, made from two lenses; he applied for a patent for this optical refracting telescope (using 2 lenses) in 1608, intending it for use as a military device. A refracting telescope uses two lenses to magnify what is viewed; the large primary lens does most of the magnification.
Liquid Paper is a quick-drying, paper-colored (white) liquid that is painted onto paper to correct printed material. Liquid Paper was invented in 1951 by Bessie Nesmith (1922-1980). It was based on white tempera paint (Nesmith was also an artist). Nesmith was a secretary in Texas, USA, before the time of word processors. She began selling her vastly popular invention, and soon ran the very successful Liquid Paper company. Her son, Michael Nesmith, was a member of the rock group called the Monkees.
Safety matches were invented by Johan Edvard Lundstrom of Sweden in 1855. Lundstrom’s new match was the first simple and safe way to make a fire. His new safety match could only be lit by striking the match against the specially-prepared surface that came attached to the box. Lundstrom put red phosphorus on the rough striking paper (on the outside the match box); the other fire-starting chemicals were on the match’s head. Previous matches gave long-time users an ailment called “phossy jaw;” this was a painful and deadly disease caused by the older matchs’ yellow phosphorus that ate into the users’ jaws.
