Glossary of Inventors and Inventions starting with the letter A.
Richard G. Drew (1899-1980) invented masking tape and clear adhesive tape (also called cellophane tape or Scotch tape). Drew was an engineer for the 3M company (the Minnesota Mining and Manufacturing).
Drew’s first tape invention was a masking tape made for painters in 1923 (this tape was designed to help painters paint a straight border between two colors). This early masking tape was a wide paper tape with adhesive on only the edges of the tape - not in the middle. Drew made an improved tape called Scotch (TM) Brand Cellulose Tape in 1930. This tape was a clear, all-purpose adhesive tape that was soon adopted worldwide. The first tape dispenser with a built-in cutting edge was invented in 1932 by John A. Borden, another 3M employee.
The forerunner of the aerosol can was invented by Erik Rotheim of Norway. On November 23, 1927, Rotheim patented a can with a valve and propellant systems - it could hold and dispense liquids.
The first aerosol can (a can than contains a propellant [a liquefied gas like flurocarbon] and has a spray nozzle) was invented in 1944 by Lyle David Goodloe and W.N. Sullivan. They were working for the U.S. Department of Agriculture and were trying to find a way to spray and kill malaria carrying mosquitos during World War II for the soldiers overseas. The “clog-free” spray valve was invented by Robert H. Abplanal in 1953.
The first spray paint was invented by Edward H. Seymour in 1949. Seymour’s wife Bonnie had given him the idea of an aerosol applicator for paint. The first spray paint he developed was aluminum colored. Seymour formed the company, Seymour of Sycamore, Inc. of Chicago, USA, which is still in operation.
The first working airplane was invented, designed, made, and flown by the Wright brothers, Wilbur Wright (1867-1912) and Orville Wright (1871-1948). Their “Wright Flyer” was a fabric-covered biplane with a wooden frame. The power to the two propellers was supplied by a 12-horsepower water-cooled engine. On December 17, 1903, the “Flyer” flew for 12 seconds and for a distance of 120 feet (37 m). The flight took place at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina, USA.
For more information on the Wright brothers, click here.
The windshield wiper was invented by Mary Anderson in 1903 to help streetcars operate safely in the rain. In 1905 she patented her invention, which allowed the car operator to control the external, swinging arm wipers from within the car. Windshield wipers became standard equipment on cars a decade later. Anderson was from Alabama, USA.
The anemometer is a device that measures the speed of the wind (or other airflow, like in a wind tunnel). The first anemometer, a disc placed perpendicular to the wind, was invented in 1450 by the Italian architect Leon Battista Alberti. Robert Hooke, an English physicist, later reinvented the anemometer. In 1846, John Thomas Romney Robinson, an Irish physicist, invented the spinning-cup anemometer. In this device, cups are attached to a vertical shaft; when the cups spin in the wind, it causes a gear to turn.
The Apgar scale is a standardized scale that is used to determine the physical status of an infant at birth. This simple, easy-to-perform test was devised in 1953 by Dr. Virginia Apgar (1909-1974), a professor of anesthesia at the New York Columbia-Presbyterian Medical Center. The Apgar scale is administered to a newborn at one minute after birth and five minutes after birth. It scores the baby’s heart rate, respiration, muscle tone, reflex response, and color. This test quickly alerts medical personnel that the newborn needs assistance.
Dr. Virginia Apgar (1909-1974), a professor of anesthesiology at the New York Columbia-Presbyterian Medical Center, devised the Apgar Scale in 1953. The Apgar scale is a simple, easy-to-perform, standardized scale that is used to determine the physical status of an infant at birth. The Apgar scale is administered to a newborn at one minute after birth and five minutes after birth. It scores the baby’s heart rate, respiration, muscle tone, reflex response, and color. This test quickly alerts medical personnel that the newborn baby needs assistance.
The aqualung is a breathing apparatus that supplied oxygen to divers and allowed them to stay underwater for several hours. It was invented in 1943 by Jacques-Yves Cousteau (1910 -1997) and the French industrial gas control systems engineer Emile Gagnan. Among the innovations in their device was a mechanism that provided inhalation and exhaust valves at the same level. That summer, the new device was tested in the Mediterranean Sea down to 210 ft (68 m) by Cousteau, Philippe Tailliez, and Frédérik Dumas. This safe, easy-to-use, and reliable device was the first modern scuba system.
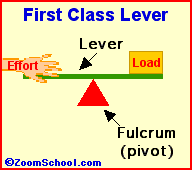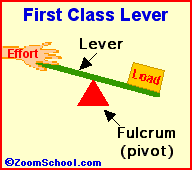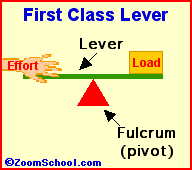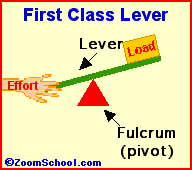
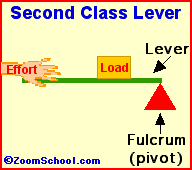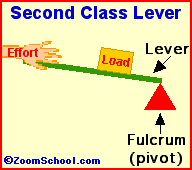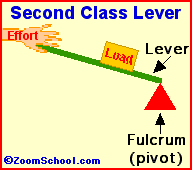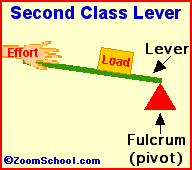
Archimedes (287-212 BC) was a prolific ancient Greek mathematician. Archimedes invented the water screw, a device for raising water using an encased screw open at both ends. The screw is set an an angle, and as the screw turns, water fills the air pockets and is transported upwards. The Archimedes screw is still in use today. Among his many accomplishments was the first description of the lever (around 260 BC). Levers are one of the basic tools; they were probably used in prehistoric times. Many of our basic tools use levers, including scissors (two class-1 levers), pliers (two class-1 levers), hammer claws (one class-1 lever), nutcrackers (two class-2 levers), and tongs (two class-3 levers).

Primitive assembly line production was first used in 1901 by Ransome Eli Olds (1864-1950), an early car-maker (he manufactured the Oldsmobile, the first commercially successful American car). Henry Ford (1863-1947) used the first conveyor belt-based assembly-line in his car factory in 1913-14 in Ford’s Highland Park, Michigan plant. This type of production greatly reduced the amount of time taken to put each car together (93 minutes for a Model T) from its parts, reducing production costs. Assembly lines are now used in many manufacturing processes.
An astrolabe is an instrument that was used to determine the altitude of objects in the sky (like the sun or stars). It was first used around 200 B.C. by astronomers in Greece. The astrolabe was replaced by the sextant.
