
 |
| Zoom Dinosaurs DINOSAUR QUESTIONS |
| Current Questions | Top 16 Questions | Old Questions | Ask A Question For Site Supporters Only |
||||
| By Date | By Type of Dinosaur | General Dino. Qns. | Qns. About Other Animals | Geological Era Qns. | |||

A: The southern Gobi desert was probably relatively dry during the late Cretaceous, when Therizinosaurus lived. (Interesting but off topic note: organisms in dry climates are more likely to fossilize, so they are over-represented in the fossil record.) Guessing a color is up to you. Safari has a Therizinosaurus model that is cream with deep green spots; that would be decent camouflage in a dry environment that had enough vegetation to sustain enough animals for Therizinosaurus to eat.
As to ghost lineages (groups of organisms that are thought to exist because of cladistic analysis, but for which there is as yet no fossil evidence of their existence), paleontologists attribute part of the problem to climate. Entire lineages may not be represented in the fossil record beause they lived in an area that is not amenable to fossilization (for example, hot wet areas, which promotes decay, not fossilization) or had certain attributes that may have inhibited fossilization (like soft or tasty flesh).
My own opinion is that there should be an early theropod that gave rise to the early birds, like Protoavis and Archaeopteryx, and you seem to be looking in a good area (although Protoavis is believed to be a chimera by some, who said it looked mis-proportioned, and thought not to have enough bird-like characters by others) - but looking at so-called oddities is probably the best way to find the flaws in the current theory. There seem to be (at least) 3 possibilities: that birds evolved from the maniraptors, when bird-like features commonly appeared in these dinosaurs (but then, where did Archaeopteryx, etc., come from?); that birds evolved from a much earlier theropod dinosaur perhaps a coelurosaur like Proceratosaurus, which pre-dated Archaeopteryx, explaining Archaeopteryx (but then, what about the maniraptors and all those nice bird-like traits?); or that birds evolved from another line entirely.
You've probably seen them already, but if not, you might find the dinosaur mailing list (hosted by the Cleveland Museum of Natural History) and Mike Keesey's site (with a Therizinosaurus on its main page) interesting.
A: Igneous rock is formed when molten rock (like lava) cools. For a fossil to be found in igneous rock, the original organism would have to have been in the lava, which is at or over 1000°C=1800°. The high temperature of the molten rock would destroy most tissues, leaving little or nothing to fossilize.
A: All the dinosaurs lived on land. For a list of dinosaur genera, click here
What people often call flying dinosaurs were called pterosaurs (like Pteranodon); they were flying reptiles who were closely related to the dinosaurs, but were not dinosaurs.
The so-called "swimming dinosaurs" were also not dinosaurs, but plesiosaurs, prehistoric reptiles that lived during the time of the dinosaurs. Some of these included Elasmosaurus and Plesiosaurus.
A: The long-necked dinosaurs, also called sauropods, ate plants (they were herbivores). For more information on dinosaur diets, click here.
A: It depends on a lot of factors, including how complete the skeleton is (especially useful is a skull), which genus it belongs to (is it a known genus or a new one), what condition the fossils are in, how hard it is to remove the rock matrix from the skeleton, etc. Sometimes, the paleontologist is later found to be wrong, and the name of the specimen is changed.
A: There are no 100 percent complete Diplodocus skeletons, so the exact number of bones is not known, but is in the vicinitiy of about 200 or so bones.
A: Argentinosaurus. For more information, see the frequently asked questions above.
A: Apatosaurus, Triceratops, and Stegosaurus. For more information on dinosaur diets, click here.
A: Triceratops means "Three-horned Face." For more information on Triceratops, click here.
A: Theropods.
A: For a page on Muttaburrasaurus, click here.
A: No, but for some information on Argentinosaurus, click here.
A: Most paleontologists take Ceratosauria and Tetanurae to be sister groups, clades that brached off from a common primitive theropod ancestor. In 'The Evolution and Extinction of the Dinosaurs,' p. 272, Fastovsky and Weishampel have alternate cladograms showing the relatioship between the two (which are sister clades in both cases). In one cladogram, the theropods branch two clades, Ceratosauria and Tetanurae. In an alternate cladogram, theropods brach into a clade containing Eoraptor and another which later branches off into a clade with Herrerasaurus, and another which eventually breaks into Ceratosauria and Tetanurae. There is also a chapter (ch. 12) in the book that discusses the traits within these groups.
A: That's a subject under debate. For information, click here.
A: On the locations page, I put all finds, synonyms or not (so you can look up where every specimen, valid or not, has been found). On the page of dinosaur genera, I try to indicate whether names are valid, dubious, synonyms, nomen nudems, etc. Let me know when your page is done - I'll put a link to it.
Coelurosaurichnus is probably the same genus as Grallator (see G. Leonardi and M.G. Lockley, 1995: A proposal to abandon the ichnogenus Coelurosaurichnus Huene, 1941: J.Vert.Paleont. 15(3, Suppl.): 40A). Coelurosaurichnus dates from the late Carnian (Triassic), roughly 220 million years ago. It had a small, three-toed tracks in which the middle toe and claw are longer than the outer ones.
Tetrapodosaurus tracks date from the early to middle Cretaceous period. For some nice pictures of this site, click here. According to Ken Carpenter, Tetrapodosaurus borealus is probably Sauropelta.
I've added Coelurosaurichnus and Tetrapodosaurus to the dictionary. You certainly keep me busy; I'll try to get to your other questions later.
A: Yes, many dinosaurs have been found in Canada (especially western Canada). For a page on Canadian dinosaurs, click here.
A: That's Compsognathus. For information on Compsognathus, click here.
A: Yes, scientists are trying to clone the recently-found woolly mammoths in Siberia with material from a modern-day elephant. For some information on woolly mammoths, click here.
A: No, it doesn't work for me either; they don't seem to use that URL anymore. The UK dinosaur society is online at: http://www.hmag.gla.ac.uk/dinosoc/.
A: The Cambrian period, also called "The Age of Trilobites," lasted from about 540 to 500 million years ago. It preceded the time of the dinosaurs by hundreds of millions of years. This was a time period in which all the existing phyla evolved! For a chart of geologic time and more information on the Cambrian period, click here.
A: Although it has been generally agreed that the remaining terrestrial dinosaurs went extinct during the K-T mass extinction 65 million years ago, a recent find in the western USA seems to indicate that there were some survivors. A single dinosaur bone was recently found in sediment that dates from the Paleocene epoch. For more information on this new find, click here.
A: There were many. For a list of the dinosaurs that have been found in Australia so far, click here.
A: The Hoatzin has small claws on the first and second wing digits when it is young (it uses the claws to climb trees). The African touraco also has wing claws when it is young. The ostrich has three claws on each wing.
A: T. rex was bigger than Carnotaurus.
A: So far, the largest is Utahraptor.
A: The blue whale.
A: Tyrannosaurus rex was up to 40 feet (12.4 m) long, about 15 to 20 feet (4.6 to 6 m) tall. It was roughly 5 to 7 tons in weight. For more information on T. rex, click here.
A: No, I haven't seen any yet.
A: T. rex was a meat-eater that counld crush bones as it ate. No one is exactly sure what its entire diet was, but it did eat Triceratops. This is known because a fragment of a Triceratops frill bone was found in a piece of fosilized T. rex dung. For more information on T. rex's diet, click here.
Tyrannosaurus rex probably lived in forests, where its prey (plant-eating dinosaurs) could find plenty of food. Fossils of different Tyrannosaurus species have been found in the USA (in Montana, Texas, Utah, and Wyoming), Canada (Alberta and Saskatchewan), and east Asia (Mongolia). For more information on where T. rex fossils have been found, click here.
A: In the 20 years since they were found, segnosaurs have been considered unusual theropods, dead-end offshoots of a prosauropod-ornithischian split, and sauropodomorphs. Curiously, Segnosaurs have characteristics of each of these groups, like toothless beaks, bird-like hips, and four-toed feet! Segnosaurs are now mostly accepted as extremely weird, advanced theropods (coelurosaurians), but this opinion is not universal.
A: For a list of the dinosaurs found in Australia, click here. I haven't heard of any dinosaurs found in Indonesia.
During the beginning of the Mesozoic Era (The time of the dinosaurs), the continents were jammed together into a supercontinent (called Pangaea), which began to break up during the Jurassic period (roughly 150 to 200 million years ago). It is around this time when Australia began to drift apart from Antarctica (see the animation below).
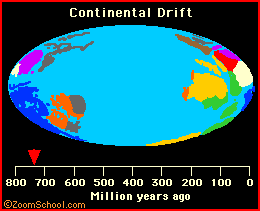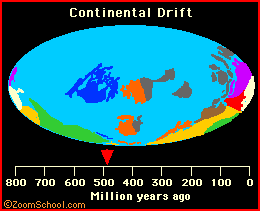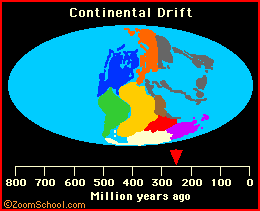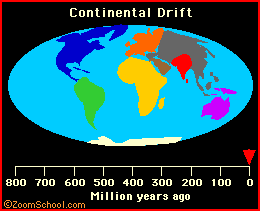 |
For more information on continental drift and plate tectonics, click here. |
A: There were probably many dinosaurs that ate fish, but only one dinosaur, Baryonyx, has been found with fossilized fish scales in its stomach. For more information on Baryonyx, click here.
A: Dinosaurs means "fearfully great lizard," Click here for more information on the word dinosaur and who coined the word.
A: No, that area was mostly underwater during the Mesozoic Era (the climate was warmer then, there was no polar ice, and the sea level was higher).
A: For information on Megalodon, a huge, extinct shark, click here.
A: It varied quite a bit (since dinosaurs ranged in size from the size of a bird to bigger than a house). The biggest dinosaurs (plant-eaters called sauropods) had footprints about the size of a bath tub.
A: Yes, dinosaurs were reptiles, and are relatively closely related to alligators and crocodiles. Dinosaurs are even more closely related to birds - one branch of the dinosaurs (some relatively small meat-eating dinosaurs) are probably the ancestor of birds.
A: Nqweba is the name of the Magisterial District of the Kirkwood formation, which is in the Algoa Basin, Eastern Cape, South Africa (Nqwebasaurus was found in the Kirkwood Formation). According to Billy de Klerk, who named Nqwebasaurus, to pronounce it, "pull you tongue of the roof of your
mouth to produce a click on the 'q'." Saurus means 'lizard.' Thwazi (pronounced TWAH-zee) is an old Xhosa (a language similar to Zulu that is spoken by the Bantu peoples of Africa) word for a fast running messenger (an almost mythical meaning, according to Billy de Klerk). For some more information on Nqwebasaurus thwazi, click here.
A: I'm not sure which is the biggest, but there have been huge dinosaur egg finds in northeastern Spain near Tremp (where hundreds of thousands of eggs of both sauropods and theropods were found), in Argentina, and in China.
A: No, people evolved roughly 64 million years after the dinosaurs went extinct.
A: Birds.
A: For a page on Pachycephalosaurus, click here.
A: I've never of Bactiosaurus, but there is a dinosaur called Bactrosaurus. Bactrosaurus or Bactrasaurus (which means 'club-spined lizard') was a large, plant-eating, duck-billed dinosaur (a lambeosaurid hadrosaurine), up to about 20 feet (6 m) long, weighing roughly 1500 kg. Its femur (thigh bone was 80 cm long. About six fragmentary Bactrosaurus fossils were found in Mongolia and China. It lived during the late-Cretaceous period, about 97-85 million years ago and was named by C.W. Gilmore in 1933. The type species is B. johnsoni.
A: Fossilized skin impressions show that Chasmosaurus' skin had small, knob-like bumps that had 5 or 6 sides. A few fossilized Centrosaurus skin impressions have been found; there's a photo of one in Discover magazine from March 1989 (the article is called 'Skinning the Dinosaur,' by Don Lessem). I've just ordered it from the library and will add a description of the skin when it arrives (probably in a few days).
A: No one knows how many dinosaurs there were. About a thousand different genera have been found so far (any many more species). Most existing fossils probably haven't been found, and most types of dinosaurs probably did not fossilize.
A: No one knows with any certainly. Click here for more information.
A: Brachiosaurus existed. For information on Brachiosaurus, click here.
A: Pterodactyloids ranged in size from having a wingspan of a few inches to almost 40 feet. Pterodactylus had a wingspan of about 30 inches.
A: Yes, many fossilized dinosaur tracks have been found.
A: The spikes were probably used mainly as protection from hungry, meat-eating dinosaurs.
A: No one knows.
A: There are no 100 percent complete T. rex skeletons, but they have about 200 or so bones.
A: Click here for the Alvarez asteroid therory. For other theories, click here.
A: I haven't heard of any. Flowering plants didn't even evolve until the Cretaceous period, and the large, fleshy fruits that we're familiair with didn't evolve until well after the dinosaurs went extinct.
A: Click here for the most widely accepted theories.
A: Apatosaurus and Brontosaurus are the same genus of dinosaur. The American paleontologist Othniel C. Marsh described and named Apatosaurus in 1877. A few years later, in 1879, he described and named another fossil, Brontosaurus. It turned out that the two dinosaurs were actually two species of the same genus. The earlier scientific name, Apatosaurus, was adopted. For more information, click here and scroll down towards the bottom of the page on Apatosaurus.
A: Synapsids are animals whose skull has an extra low opening behind the eyes; this opening gave these animals stronger jaw muscles and jaws (the jaw muscles were anchored to the skull opening). Synapsids include the mammals, and extinct animals such as Dimetrodon. The pelycosaurs were early synapsids; later synapsids were the therapsids, cynodonts and dicynodonts (from the late Permian), leading to the mammals. With time, the synapsid gait became more upright and tail length decreased. The oldest-known synapsid is Archarothyris, a pelycosaur 300 million years old.
A: For a page on Megalodon, click here.
A: Dinosaurs have been found on all seven continents and lived in a variety of environments.
A: Walon Green, John Harrison and Robert Nelson Jacobs.
A: The paleontologist Henry F. Osborn was the first paleontologist to give dinosaurs raptor names. He named Oviraptor and Velociraptor in 1924. "Raptor" means thief or robber, so these dinosaurs names meant "egg thief" and "speedy thief" respectively. Lately, many people call the dromaeosaurid dinosaurs raptors. In the past, raptors referred only to raptorial birds, like eagles and falcons.
A: Dinosaurs lived during the Triassic period, the Jurassic period, and the Cretaceous period. These three periods together are called the Mesozoic Era.
A: For early Cretaceous dinosaurs, click here. For middle Cretaceous and late Cretaceous dinosaurs, click on the links at the top of the Cretaceous page.
A: The phoenis is a mythical bird - it never existed xcept in Arabian legends. It was supposed to have been a beautiful bird that lived for hundreds of years, then burned itself up, and arose from its own ashes.
A: Abelisaurus is known from only a partial skull. It was roughly 21 to 25 feet (6.5 to 8 m) long.
A: Coal (called a fossil fuel) is made of ancient plant material that has been compressed and heated for millions of years. Fossils (like dinosaur fossils) are formed when minerals replace the original chemicals in an organism, forming a rock-like replica of the original. I've never heard of a fossil made of coal.
Yes, many animals fossilize as the result of volcanic eruptions. During volcanic eruptions, tremendous pyroclastic flows (tons of fragmented rock, ash, pumice, earth, mud, etc. ejected from the volcano) kill and immediately bury many living things. This quick burial makes fossiliziation more likely, and some of these organisms do turn into fossils over time.
A: No, although they are both mammals (Class Mammalia). Bears belong to the Order Carnivora and Family Ursidae (7 species of bears). Pigs belong to the Order Artiodactyla (even-toed hoofed mammals) and Family Suidae (8 species of pigs).
A: The biggest-known dromaeosaurid is Utahraptor. I doubt that any of them were mean - just hungry.
A: For a page on the American crocodile, click here.
A: First, I'm not a man. Second, Tsintaosaurus is only known from two skulls and a few bones, so its tail length, stomach size, speed, etc., are not known. Tsintaosaurus is a doubtful name and is probably the same as Tanius (which was named earlier and therefore retains its name), a crestless hadrosaurid from China.
A: Aachenosaurus (meaning "Aachen lizard") was named by Smets in 1888. Only some "jaw fragments" were found, but they were later determined to be petrified wood.
A: Click here for dinosaur naming conventions.
A: Deinodon (meaning "terrible tooth") was a meat-eating dinosaur from the late Cretaceous period. This Coelurosaurid theropod is only known from a dozen large, fossilized teeth collected by Dr. F. V. Hayden by the Judith River in Montana, USA. Deinodon was named by paleontologist J. Leidy in 1856. Deinodon is a dubious genus [nomen dubium]. It may be the same genus as Gorgosaurus or Albertosaurus.
A: None. The dinosaurs evolved roughly 230 million years ago and went extinct 65 million years ago. Only simple life forms were around 600 million years ago (during the Vendian period).
A: Quaesitosaurus lived during the late Cretaceous period, about 85 to 80 million years ago. It wandered into the Triassic list compeletly by mistake (which has been fixed).
A: Dinosaur eggs varied in size from about an inch in diameter (Mussaurus) to football sized (Hypselosaurus). For a page on dinosaur eggs, click here.
A: Click here.
A: Different dinosaurs had different means of defense. Some had armored plates (like Ankylosaurus), some had horns (like Triceratops), some had whip-like tails (like Diplodocus), some had bludgeon-like tails (like Euoplocephalus), and many had beaks and claws. Hugeness protected some dinosaurs (like Apatosaurus), running away protected many others (like Iguanodon), and some may have butted enemies with thei head (like Stegoceras). For more information on dinosaur defenses, click here. For a printout on dinosaur defenses, click here.
A: There haven't been any dinosaur fossils found in some states. Some of the states (like Florida) were underwater for part or or most of the Mesozoic Era (when sea levels were much higher than they are now, since there was no polar ice during most of the warm Mesozoic). Some states have little or no exposed Mesozoic Era sedimentary rock (like Washington state), making dinosaur-era fossils virtually impossible to find.
A: Not very closely. Giraffes are mammals (like we are); dinosaurs were reptiles. Reptiles and reptile-like mammals (synapsids, which eventually evolved into mammals) branched off during the Carboniferous period, about 300 million years ago.
A: The earliest-known dinosaurs are two as yet un-named plant-eaters that date from about 230 million years ago (found in Madagascar) and Eoraptor, a meat-eater from Argentina.
A: Only one has been found (in Argentina, South America). Carnotaurus was about 25 feet (7.5 m) long and weighed about 1 ton (1000 kg). For more information on Carnotaurus, click here.
A: Dacentrurus was a stegosaurid that had two rows of small, asymmetrical plates on its back and two rows of long spikes (with sharp edges) running along its lower back and tail. The long spikes were almost certainly protection for this plant-eating dinosaur. Paleontologists have found fossil evidence of etensive vascularization (a system of blood vessels) in the plates of other Stegosaurids (like Stegosaurus). These blood vessels suggest that the plates served to regulate the animal's temperature. When it wanted to cool down, heat could be dissapated from th eplates; when it wanted to warm up, it could sun itself, exposing the blood in the plates to warming sunlight.
A: Many paleontologists think that some theropod dinosaurs (maniraptors) evolved into birds. For more information, click here.
A: Saltasaurus was a long-necked plant-eating dinosaur about 40 feet (12 m) long. For more information on Saltasaurus, click here.
A: For a list of Australian dinosaur fossils, click here.
A: Oviraptor was an omnivore (eating both plants and meat).
A: Tyrannosaurus rex, like all dinosaurs, are commonly known by their scientific name. Tyrannosaurus is its genus; rex is its species. For more information on T. rex, click here.
A: Dinichthys (meaning "terrible fish"), was a family of ancient, meat-eating fishes. Dunkleosteus was the biggest member of this family. For information on Dunkleosteus, click here.
A: No, because none of the dinosaurs lived in the water (they didn't have flippers, and weren't adapted to life in the water). There are some people who think that the Loch Ness monster may be a plesiosaur (a marine reptile that lived during the time of the dinosaurs).
A: No, we don't, but there are a lot of sites that sell fossils (and have a lot of pictures). Go to a search engine (like Google.com) and search using the words "fossils dinosaur eggs," or other words to that effect, and a lot of fossil shops will appear.
A: There are roughly 1,000 known dinosaur genera, and many more species - for more information, click here. What type of theories are your asking about - there are theories for just about everything? Many things aren't known with 100% certainty, so the word "probably" is often used. No, the dinosaurs probably (see the previously answers) weren't exactly as depicted in museums. Your other questions are answered in the faq's above (which you should have read first). For a discussion on dinosaur metabolism (cold-blooded or warm-blooded), click here. If you don't visit again, how could you possibly even know if I answered your question?
A: The USA has the most so far, but that's mostly because people here have looked more, there are a lot of exposed, eroded areas, and the USA is a large country. In many other parts of the world, paleontologists haven't even begun to look for fossils yet (because of the difficulty of getting to and from remote places, long-standing, dangerous political conflicts, and/or a lack of cooperation from bureaucrats). In the last few years, a tremendous amount of incredible fossils have been found in China, Antarctica, Africa, and South America. The next few years should be very interesting, as more and more places are explored for fossils.
Return to the top of the page.
Enchanted Learning®
Over 35,000 Web Pages
Sample Pages for Prospective Subscribers, or click below
|
Overview of Site What's New Enchanted Learning Home Monthly Activity Calendar Books to Print Site Index K-3 Crafts K-3 Themes Little Explorers Picture dictionary PreK/K Activities Rebus Rhymes Stories Writing Cloze Activities Essay Topics Newspaper Writing Activities Parts of Speech Fiction The Test of Time
|
Biology Animal Printouts Biology Label Printouts Biomes Birds Butterflies Dinosaurs Food Chain Human Anatomy Mammals Plants Rainforests Sharks Whales Physical Sciences: K-12 Astronomy The Earth Geology Hurricanes Landforms Oceans Tsunami Volcano |
Languages Dutch French German Italian Japanese (Romaji) Portuguese Spanish Swedish Geography/History Explorers Flags Geography Inventors US History Other Topics Art and Artists Calendars College Finder Crafts Graphic Organizers Label Me! Printouts Math Music Word Wheels |
Click to read our Privacy Policy
| Search the Enchanted Learning website for: |